The use of ultrasound has increased steadily in recent years. Its rise is driven by an aging population, increasing chronic disease, and the need for cost-effective, radiation-free, non-invasive diagnostics. Philips has redefined ultrasound performance by utilizing NVIDIA technology across its comprehensive portfolio—including cardiology, general imaging, obstetrics, gynecology, and point-of-care applications.* This article was originally published by NVIDIA. NVIDIA is a technology company that specializes in artificial intelligence computing.
Philips Ultrasound faced challenges that were constraining innovation and patient care delivery. On the development side, the company sought faster iteration cycles in algorithm development, while managing increasingly complex parallel processing demands that strained their traditional hardware-based architecture.
Clinically, ultrasound imaging remained highly patient-dependent with significant variability across different patients and scenarios. Healthcare providers needed more robust imaging that could adapt automatically, deliver higher-resolution 3D volumes at better frame rates and offer advanced tools for visualizing complex anatomy—particularly during interventional procedures and in women’s healthcare applications.
To accelerate innovation and support increasingly advanced imaging techniques, Philips transitioned its ultrasound platform from custom FPGA-based hardware to software-defined beamforming for its third generation. Powered by NVIDIA RTX professional GPUs, this transformation delivers the high-performance, energy-efficient computing needed for real-time beamforming. The result is sharper images, faster processing and more confident diagnoses, helping clinicians deliver better care, more efficiently.
Using NVIDIA's CUDA framework, Philips unlocked massive parallel processing capabilities, transforming ultrasound imaging performance. CUDA specifically accelerates core imaging functions — from beamforming, filtering, and envelope detection to post-processing algorithms like Image Boost—while the GPU's immense computational power drives advanced 3D data reconstruction and volume rendering. This comprehensive software-defined architecture enables real-time adaptive imaging that responds dynamically to each patient's unique acoustic window and anatomical characteristics, without requiring full system overhauls.
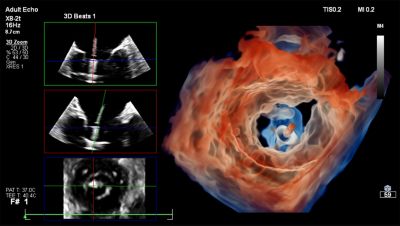
Migrating to NVIDIA RTX GPUs cut years of R&D to months. CUDA enables rapid iteration and integrates advanced algorithms, delivering real-time, photorealistic 3D cardiac imaging—helping clinicians diagnose faster, treat sooner, and improve outcomes.
The software-defined architecture delivers transformative benefits that extend well beyond traditional performance metrics. The jump in performance capabilities of GPU-based beamforming compared to FPGA allows a 70% improvement in 3D Color volume rates, one of the most computationally intensive ultrasound modes. The flexibility of software-defined architecture enables the advanced signal processing necessary to maintain image quality, which the laws of physics previously required to be sacrificed to achieve these real-time volume rates. The result allows clinicians to visualize pathologic flow in real time across the complex structures of the heart valves.
The implementation of NVIDIA GPU beamforming technology has delivered measurable results across multiple dimensions of performance and business value. Performance improvements from the latest generation of GPUs can be brought to customers faster and simpler through a flexible, modular design with the aim of reducing total cost of ownership.
By migrating to GPU-based beamforming, Philips has accelerated its innovation cycle. Through NVIDIA’s CUDA platform, a broader team of engineers, not just hardware specialists, can contribute to developing, testing and improving algorithms, leading to faster time to market and reduced development costs. The software-defined architecture also supports sustainability goals. Furthermore, by reducing its reliance on custom hardware, Philips has achieved a more modular design, thereby minimizing waste and extending system performance through software upgrades. The GPUs’ energy-efficient processing further contributes to greener operations.
The advanced parallel processing of GPU beamforming enables Philips to form 3D cardiac volumes at near-2D frame rates and resolutions, providing sonographers with a real-time view of complex cardiac anatomy that traditional beamformers cannot deliver. Adaptive GPU-based imaging algorithms automatically adapt to each patient's unique acoustic window, producing more consistent and high-quality images across the entire patient population without requiring extra operator intervention or contrast agents.
In clinical practice, these capabilities are designed to translate into faster, more confident diagnoses, fewer repeat scans or modality referrals and smoother workflows. Real-time 3D cardiac imaging is also accelerating innovations in minimally invasive intracardiac valve replacement and repair surgeries, providing life-changing options for hundreds of thousands of patients who wouldn't have been candidates for open-heart surgery.
NVIDIA’s GPUs have transformed our engineering velocity and sustainability. By developing algorithms through CUDA, we accelerate innovation, reduce hardware reliance and costs and deliver faster imaging with efficiency and environmental benefits.
GPU beamforming enhances diagnostic confidence, thereby reducing the need for clinicians to interpret ambiguous ultrasound images. Improved image quality eases the burden of difficult cases, enabling consistent exams and smoother workflows. In procedural settings, GPU-enabled systems support demanding imaging for minimally invasive interventions, expanding access and reducing costs.
Philips’ scalable GPU platforms allow future upgrades via software, preserving capital investment and ensuring long-term value. Technologies like TrueVue and GlassVue—Philips’ advanced 3D imaging solutions— directly benefit from GPU acceleration, delivering photorealistic images that enhance depth perception and anatomical understanding in real time.
Philips' transformation from FPGA-based to GPU-accelerated ultrasound imaging demonstrates how NVIDIA's accelerated computing platform enables medical device manufacturers to break through traditional hardware limitations while delivering superior clinical outcomes. By transitioning from rigid, custom hardware systems to flexible, software-defined architectures, Philips has established a foundation for continuous innovation that directly benefits both healthcare providers and patients through enhanced diagnostic capabilities, improved workflow efficiency, and expanded treatment options for complex cardiac procedures.