Philips Liver Fat Quantification
Ultrasound-based liver fat quantification methods have gained attention due to the need for a widely accessible non-invasive imaging biomarker for fatty livers. The Philips Liver Fat Quantification (LFQ) solution allows measurement of liver attenuation and characterization of relative echogenicity. It provides simple, intuitive tools for managing chronic liver disease.

Fatty liver disease is the most common and earliest stage of chronic liver disease, with a global prevalence of about 25% [2]. This includes simple liver steatosis and more severe forms such as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), fibrosis and cirrhosis. Early assessment of fatty liver is crucial for potentially reversing the progression of the disease.
Traditionally, liver biopsies have been used for diagnosing fatty liver disease, but they come with risks and limitations. Magnetic resonance imaging-derived proton density fat fraction (MRI-PDFF) has become a widely adopted noninvasive method for quantifying liver fat. However, the cost and limited access to MRI can be a challenge for many.
Ultrasound-based liver fat quantification methods have gained increased attention recently due to the need for a widely accessible noninvasive imaging biomarker to address the prevalence of fatty livers [1].
Ultrasound-based liver fat quantification methods have gained increased attention recently due to the need for a widely accessible noninvasive imaging biomarker to address the prevalence of fatty livers.
Clinicians have long recognized that the presence of fat in the liver generates a smooth, hyperechogenic appearance in the liver, especially when compared to the echogenicity of the adjacent kidney. Fat also increases the attenuation of the liver, thereby reducing the ultrasound penetration and the visualization of the deeper structures such as the diaphragm. The Philips Liver Fat Quantification (LFQ) solution allows the user to measure the attenuation of the liver using the attenuation quantification tool and characterize the relative echogenicity of the liver using the hepatorenal index (HRI) tool.
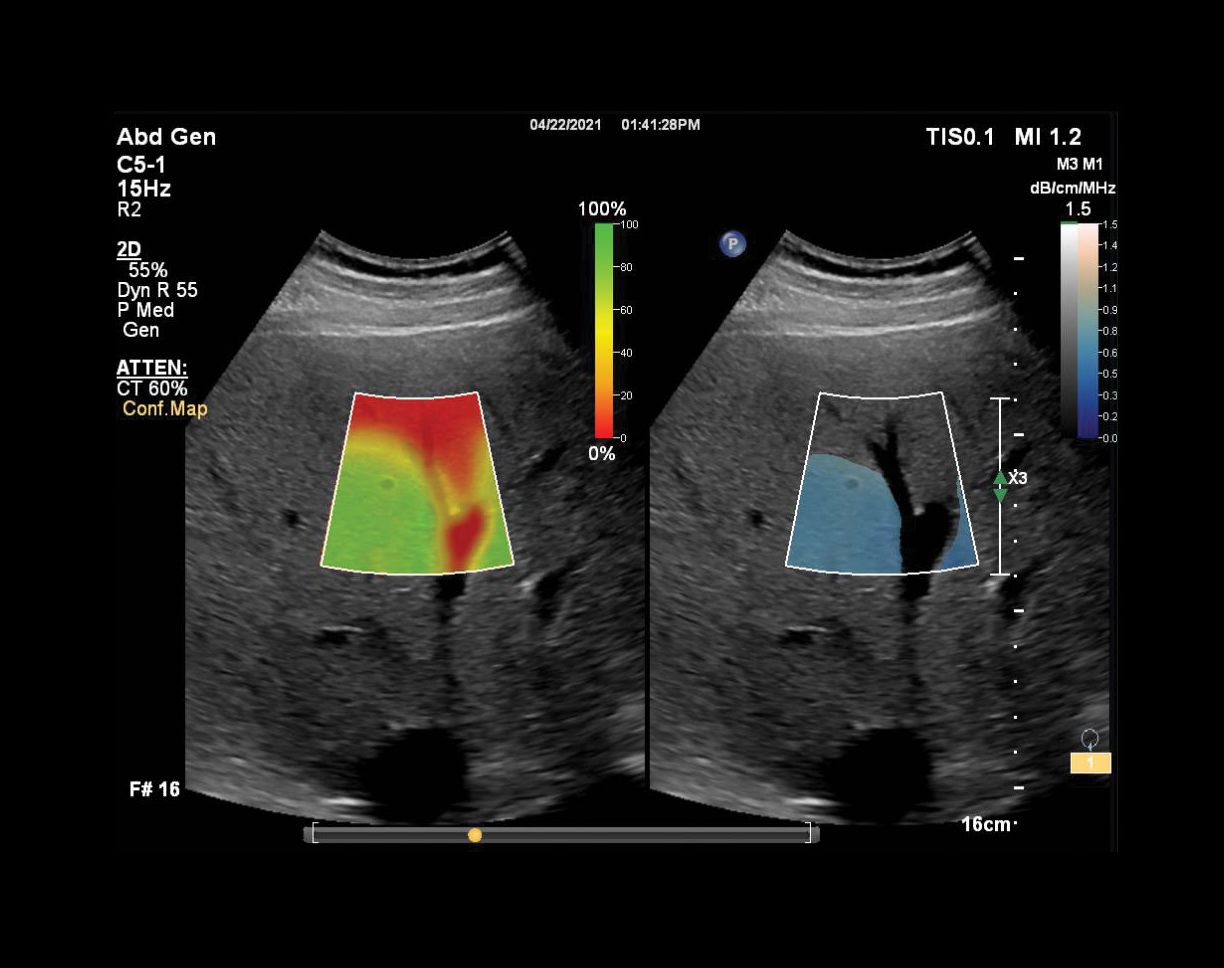
The LFQ solution also includes a hepatorenal index (HRI) tool, which measures the ratio of echo amplitude between the liver and kidney. HRI has been used clinically for fatty liver detection and can be calculated using ultrasound images.
The Philips Liver Fat Quantification solution provides simple and intuitive tools for physicians to manage patients with chronic liver disease. It supports the delivery of accurate and reproducible measurements of liver attenuation and characterization of liver echogenicity.
Clinical studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of the LFQ solution in quantifying liver fat and its correlation with MRI-PDFF measurements. LFQ can assist in managing patients with fatty liver disease and potentially reverse the progression of the disease.
