Gingival health
In-vivo study
A randomized, parallel study to compare Philips Sonicare Power Flosser and interdental brush on reducing gingival bleeding and plaque
Amini P, Imtiaz U, Li J, Ward M, Nelson M, Foster J Silverstone Research Group, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2020 Data on file

Objective
The objective of this study was to compare the effects of manual toothbrushing plus two different interdental cleaning modalities, compared to manual toothbrushing alone, on gingivitis, gingival bleeding and plaque levels following a home use period of four weeks, and to assess the safety of the test products.
Methodology
This was a three-arm, IRB-approved, single-blind, randomized, parallel clinical trial conducted in a generally healthy population of adults in the United States. Eligible subjects were aged 18–65 years, non-smokers and with no or infrequent interdental cleaning habits (less than once per week). Subjects were to have a minimum plaque score of at least 0.6, as scored by the Rustogi Modified Navy Plaque Index (RMNPI) following a three- to six-hour plaque accumulation period, as well as a gingival bleeding score of 1.0 on at least 50 sites, as scored by the Gingival Bleeding Index (GBI). Eligible subjects were randomized to one of three treatment groups: manual toothbrushing alone (MTB), manual toothbrush plus TePe® interdental brush (IDB), or manual toothbrush plus Philips Sonicare Power Flosser with Quad Stream nozzle (PFQS). The Colgate Classic adult manual toothbrush and a standard dentifrice were dispensed to all groups and were used twice daily. Those randomized to IDB or PFQS performed adjunctive interdental cleaning once daily. The use of any other oral hygiene product or procedure was not permitted during the study period. Subjects were provided a diary to record compliance to the assigned regimen, as well as to document any safety events. Subjects returned to the clinic at Week 2 for an interim assessment of plaque and gingival health status, and at Week 4 for final evaluation, product return and dismissal from study.
Results
There were 207 subjects screened, with 189 subjects enrolled and randomized to one of the three treatment groups: MTB (n=64), MTB+IDB (n=62), and MTB+PFQS (n=63). Of the 189 randomized subjects, 186 (98.4%) completed the study. There were 119 (63%) females and 70 (37%) males. The mean age of all randomized subjects was 37.2 (SD=12.5) years. The overall distribution of race was white: 102 (54%), Black or African heritage: 42 (22.2%), Asian: 22 (11.6%), Native Hawaiian or other Pacific Islander: 13 (6.9%), and other: 10 (5.3%). For ethnicity, 44 (23.3%) of subjects randomized were Hispanic or Latino. There were no significant differences in the treatment groups for demographic and baseline characteristics, including for plaque per RMNPI (p-value = 0.7351), gingival bleeding per GBI (p-value = 0.6738) and gingival inflammation per Modified Gingival Index, MGI, (p-value = 0.0952). Efficacy
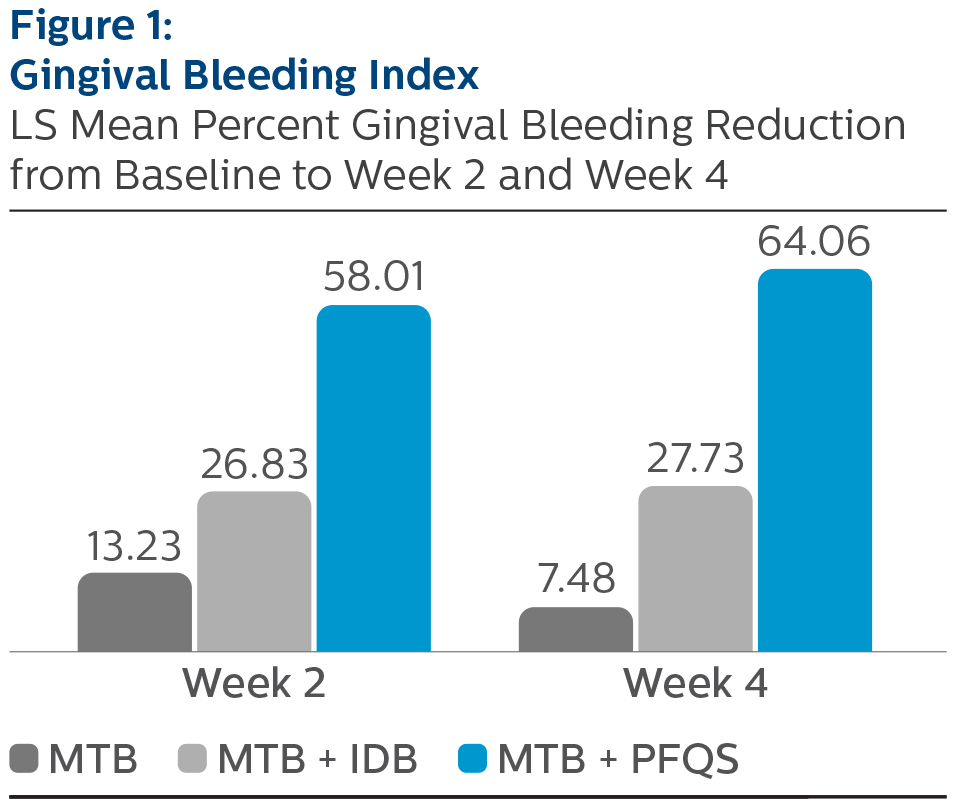
Gingival Bleeding Index:
LS Mean (SE) Baseline and Percent Reduction from Baseline Values
| |
|
|
|
| Baseline | | | |
| Percent Reduction from Baseline | | | |
| Week 2 | | | |
| Week 4 | | | |
*Pairwise comparisons were statistically significant verses MTB treatment group, p-value < 0.0001 ^Pairwise comparisons were statistically significant versus MTB + IDB treatment group, p-value <0.0001
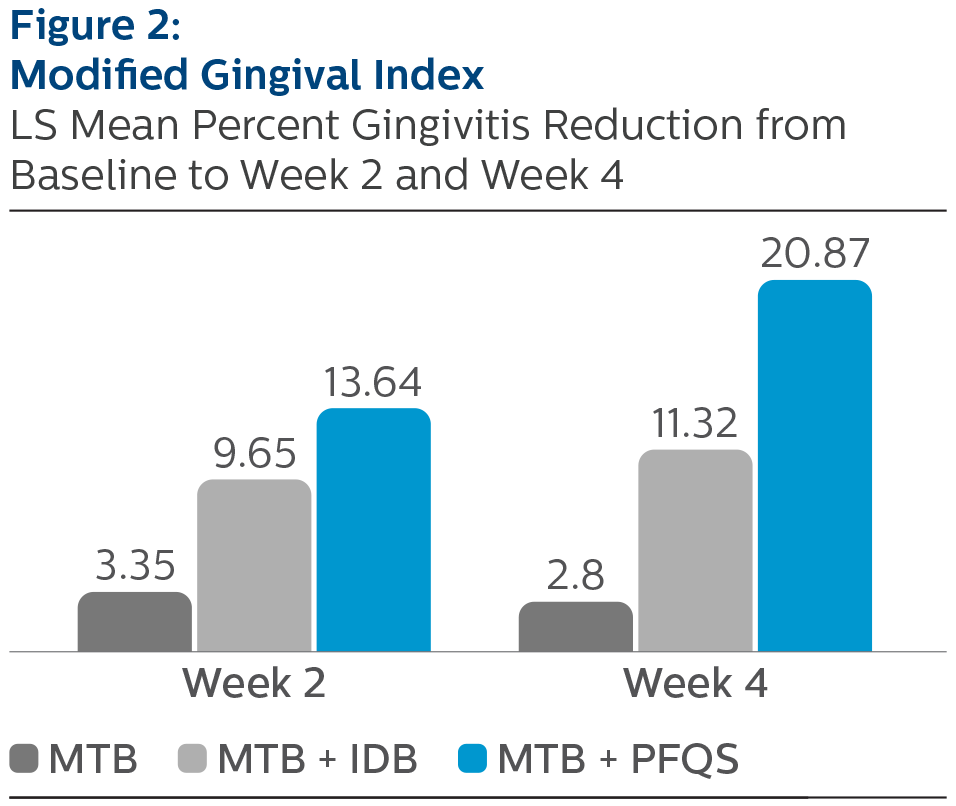
Modified Gingival Index:
LS Mean (SE) Baseline and Percent Reduction from Baseline Values
| |
|
|
|
| Baseline | | | |
| Percent Reduction from Baseline | | | |
| Week 2 | | | |
| Week 4 | | | |
*Pairwise comparisons were statistically significant verses MTB treatment group, p-value < 0.0001 ^Pairwise comparisons were statistically significant versus MTB + IDB treatment group, p-value <0.0001
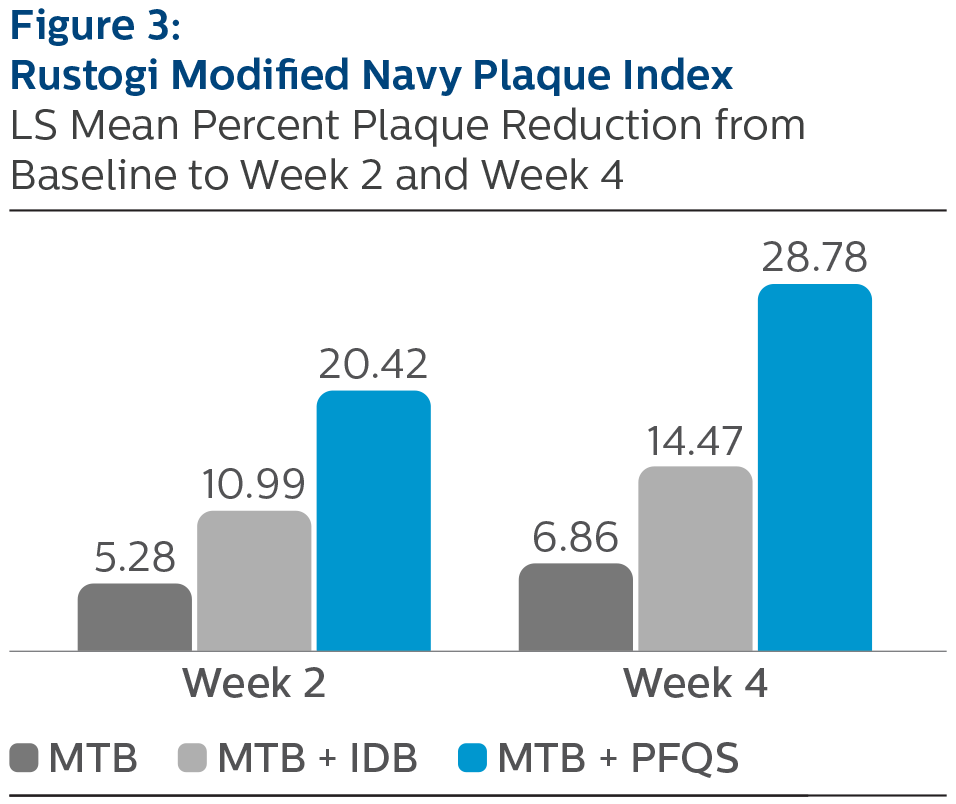
Rustogi Modified Plaque Index:
LS Mean (SE) Baseline and Percent Reduction from Baseline Values
| |
|
|
|
| Baseline | | | |
| Percent Reduction from Baseline | | | |
| Week 2 | | | |
| Week 4 | | | |
*Pairwise comparisons were statistically significant verses MTB treatment group, p-value < 0.0001 ^Pairwise comparisons were statistically significant versus MTB + IDB treatment group, p-value <0.0001
Safety There were 21 reported adverse events among 19 subjects, 14 of which were possibly related to the study, 2 in the MTB group, 10 in the MTB+IDB group, and 2 in the MTB+PFQS group. All events were characterized as mild in severity.
Conclusions
All three treatment groups exhibited improvements in GBI, MGI, and RMNPI compared to baseline after two and four weeks of at-home use. The use of the Philips Sonicare Power Flosser, as an adjunct to manual toothbrushing, demonstrated the largest magnitude of reduction in gingival inflammation, bleeding and dental plaque, followed by manual toothbrush plus interdental brush, and manual toothbrush alone, at both two weeks and four weeks. Comparisons between products yielded statistically significant differences between the Philips Sonicare Power Flosser, the interdental brush, and manual toothbrush alone, for all measures, at both timepoints. All study products were safe for use.
© 2021 Koninklijke Philips N.V. (KPNV ). All rights reserved. PHILIPS and the Philips shield are trademarks of KPNV. SONICARE and the Sonicare logo are trademarks of KPNV. Data on file - Protocol ID OHC_10759
1 Jan, 2021 by Philips
Reading time: 4-5 minutes
Share on social media
Contacts

Sarah Berryhill
Clinical Marketing Team
You are now exiting the Philips United States (US) site and entering the Philips global site. This content is intended for a global audience. It may not apply to the US and should not be interpreted as meeting US standards, executive orders or regulations.
Continue Assets